GraphHopper Directions API Integration Guide
Integrate the GraphHopper Directions API to calculate road distance between pickup and delivery locations, and store the result on the Load record in FTM.
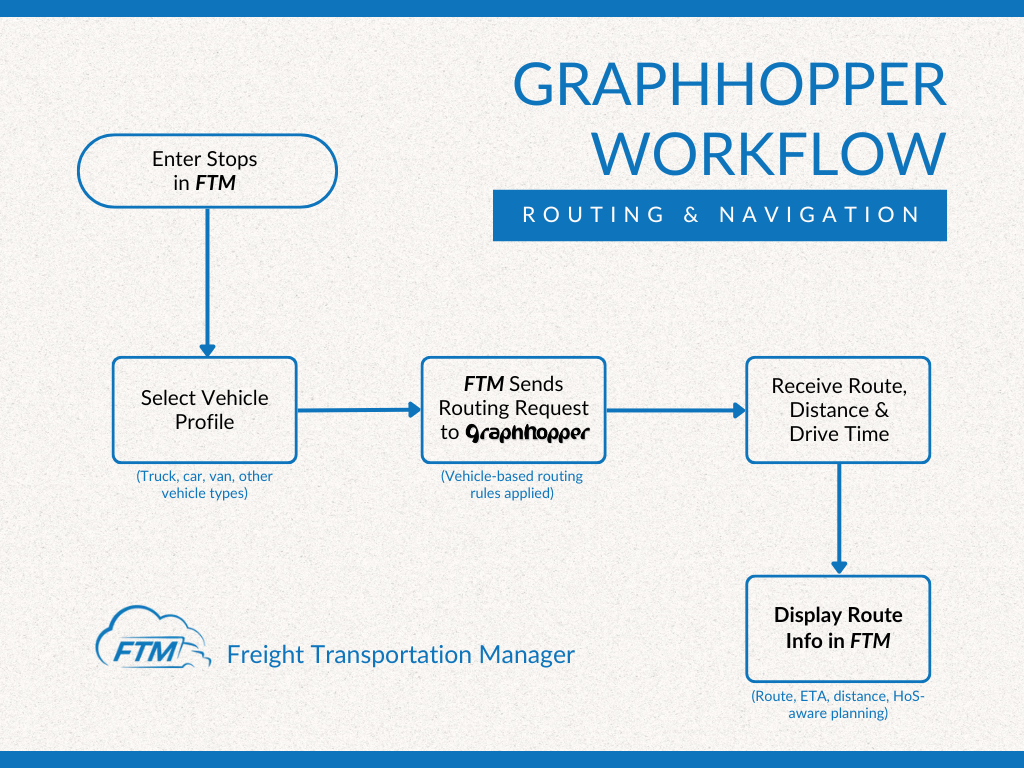
Overview
This integration connects FTM with the GraphHopper Directions API to calculate the point-to-point distance between pickup and delivery facilities. The result is stored in the FreightTM__Distance__c field on the FreightTM__Load__c object. The integration runs asynchronously, ensuring that the UI remains responsive.
Key Components
- Apex Class: GraphHopperQueueable (Queueable + callout)
- External Service: GraphHopper Directions API
/route - Data:
FreightTM__Load__c+ relatedFreightTM__Facility__c(with coordinates)
What This Integration Does
- Takes two coordinates (Pickup & Delivery).
- Calls GraphHopper Routing API with a chosen profile (default is car).
- Extracts paths[0].distance (in meters) from the response.
- Converts meters to kilometers and stores it in FreightTM__Distance__c.
- Runs asynchronously to ensure the UI remains responsive; it is safe to enqueue from Flow/Apex.
Setup Requirements
- GraphHopper API Key
– Create/get an API key in your GraphHopper account.
– Do not hard-code the API key; store it securely (use step 3 below). - Salesforce Callout Allowlist
– Add Remote Site Settings forhttps://graphhopper.com(or use Named Credential). - Recommended: Named Credential + Protected Storage
– Use Named Credentials (URL:https://graphhopper.com/api/1/).
– Store the API key in Protected Custom Metadata/Setting (org-wide) and append&key=…at runtime.
Note: GraphHopper expects the key as a query parameter. Named Credentials don’t add it automatically. - Permissions
– Ensure Apex Class access toGraphHopperQueueable.
– CRUD/FLS toFreightTM__Load__c.FreightTM__Distance__c.
– Read access to related Facility coordinates (Coordinates__c). - Facility Coordinates Present
– Ensure both Pickup and Delivery Facilities have valid Geolocation values inCoordinates__c(latitude and longitude). - Attribution
– GraphHopper uses OpenStreetMap data. If you display maps or route results, include appropriate attribution within your UI per licensing.
How It Works
- A process (Flow, Apex, button, or Scheduler) enqueues GraphHopperQueueable with a list of Load Ids.
- The job queries Loads and related Pickup/Delivery Coordinates__c.
- For each Load with both coordinates present:
– Build a GET/routerequest with two point parameters (lat, lon), profile=car (or other), andkey=<API_KEY>.
– Send the callout and parse the JSON response.
– Read paths[0].distance (in meters) and convert to kilometers.
– Update FreightTM__Distance__c on the Load. - Loads missing coordinates are skipped with a debug note.
Field Mapping
Inputs (from Salesforce)
| Object | Field | Purpose |
| FreightTM__Facility__c | Coordinates__c | Start latitude/longitude |
| FreightTM__Facility__c | Coordinates__c | End latitude/longitude |
Output (to Salesforce)
| Object | Field | Value |
| FreightTM__Load__c | FreightTM__Distance__c | Route distance in kilometers (rounded) |
API Response → Fields
| GraphHopper JSON Field | Meaning | FTM Use |
| paths[0].distance | Total route distance in meters | Yes (convert to kilometers) |
| paths[0].time | Total travel time in milliseconds | Not used (optional future) |
Implementation
- Secure the API key:
– Create Protected Custom Metadata/SettingGraphHopper_Config__mdtwith a fieldAPI_Key__c.
– Reference it in Apex instead of hard-coding. - Switch Endpoint to Named Credential:
– Use the following code to set the endpoint and pass the API key from Protected Metadata.String base = 'callout:GraphHopper/route';
String params = '?point=' + startPoint.getLatitude() + ',' + startPoint.getLongitude() +
'&point=' + endPoint.getLatitude() + ',' + endPoint.getLongitude() +
'&profile=' + 'car' +
'&key=' + GraphHopper_Config__mdt.getInstance('Default').API_Key__c;
request.setEndpoint(base + params); - Avoid Duplicate Calls:
– Only enqueue when either facility coordinate changed orFreightTM__Distance__cis blank/stale.
– Use a before/after save Flow or Apex trigger with change detection. - Rounding & Units:
– Store distance asrouteMeters / 1000.0. Optionally round to 1–2 decimals for UI. - Bulk Patterns:
–executealready handles multiple Loads. Keep per-transaction API calls within GraphHopper rate limits.Add Limits.getCallouts()checks as guard rails. - Error Handling:
– Log status codes and response body on non-200 responses.
– Consider a small retry/backoff for transient 5xx errors.
– For persistent failures, add a platform event or a custom error object for ops visibility. - Matrix API for Many Pairs:
– For bulk origin-destination distances (e.g., computing a lane matrix), use the Matrices API and update your persistence model accordingly. - Optional Custom Profiles:
– For truck constraints (heights, weights), use small_truck or truck profiles (paid) or define custom profiles (premium) and reference them via theprofileparameter.
Common Issues
- 401/403 Unauthorized:
– Invalid or missing API key. Ensure&key=is appended correctly. - 429 Rate Limit:
– Exceeded your plan’s QPS/credits. Reduce concurrency, add jittered retries, and cache distances. - Empty
pathsArray:
– Points too close, off-network, or in the ocean; or profile not available on your plan. - Null Coordinates:
– Ensure both Facilities have coordinates populated. Skip gracefully when missing. - Hard-coded Key in Code:
-Security risk. Move to protected storage and audit your repo. - URL Too Long:
– When adding more parameters, switch to POST /route and set JSON body.
Limitations
- The free plan supports only car, bike, and foot profiles. Heavy vehicle profiles require paid plans.
- No live traffic in standard OSM routing; TomTom add-on currently applies to Route Optimization, not base Routing.
- Rate limits/credits apply. Bursts may be throttled.
- Data coverage/accuracy depends on OSM and your package region.
- Single-pair focus: For N×M distances, use Matrices API.
FAQs
- What profile should I use?
carby default. For fleets, consider small_truck or truck (paid). You can also build a Custom Profile (premium) to reflect restrictions. - Does GraphHopper return time as well?
Yes.paths[0].timein milliseconds. You can store this in a custom field if needed. - Can I use POST instead of GET?
Yes, and it’s recommended for complex requests (custom models, many params) and to avoid URL limits. - How do I stay within rate limits?
Batch Loads, respect QPS, add backoff on 429/5xx errors, and cache distances when inputs haven’t changed. - Can I compute many distances at once?
Use the Matrices API for efficient N×M travel times/distances. - Do I need to show attribution?
If you display maps or route data publicly, include attribution for OpenStreetMap/GraphHopper per licensing. - How do I trigger the queueable flow?
Create an Invocable Apex that accepts a list of Load IDs and enqueues GraphHopperQueueable. Call it from an After-Save Record-Triggered Flow when coordinates change. - Can I add via points?
Yes. Add morepoint=parameters (GET) or an array in POST. Distance will reflect the full route.
GraphHopper Route Optimization (VRP) Integration Guide
Integrate the GraphHopper Route Optimization (VRP) API with FTM to sequence trip stops, optimize routes, and calculate accurate distance and time for trips.
Overview
This integration connects your FTM environment to the GraphHopper VRP API, enabling per-trip optimization and the calculation of accurate distance and time values for routes.
What It Does
- Sequences trip stops optimally for one vehicle (closed-loop routing)
- Handles business rules for load prioritization (e.g., high-priority loads first)
- Calculates and updates distance and time metrics for Trips and Loads
- Works asynchronously, triggered by Flow, Apex, or manual button clicks
Key Components
- Apex Class:
GraphHopperOptimizer(Queueable Apex) - External Services: GraphHopper Route Optimization (
/vrp,/route) - Data:
FreightTM__Trip__c, FreightTM__Load__c, coordinates (pickup/delivery)
Setup Requirements
1. GraphHopper API Key
- Create a GraphHopper API key from the GraphHopper Developer Portal.
- Store the API key securely in Protected Custom Metadata (e.g.,
GraphHopper_Config__mdt.API_Key__c).
2. Salesforce Callout Allowlist
- Add Remote Site Settings or a Named Credential for
https://graphhopper.com/api/1/. - Recommended: Use Named Credentials to handle the base URL and append the API key dynamically.
3. Named Credential + Secure Key Handling
- For best security practice, use Named Credentials for API communication and Custom Metadata for API key storage.
- Construct requests like:
callout:GraphHopper/vrp?key=<API_KEY>
4. Permissions
- Apex Class: Access to
GraphHopperOptimizer(Queueable) - Field Permissions: CRUD/FLS on
TripandLoadfields (Total_Distance__c,Estimated_Driving_Time__c, Route_Sequence__c) - Coordinates: Access to
Coordinates__Latitude__s,Coordinates__Longitude__son Warehouse and Load records.
5. Facility Coordinates
- Ensure that Warehouse facilities have valid latitude/longitude coordinates (
Coordinates__Latitude__sandCoordinates__Longitude__s). - Ensure Loads have proper pickup/delivery coordinates.
How It Works
1. Query Depot & Stops
- Depot Coordinates are pulled from the Warehouse record linked to the Trip.
- Service Stops are fetched from the Load records (delivery coordinates).
2. Build VRP Payload
The VRP payload is constructed with:
- One vehicle starting at the depot
- Return-to-depot set to
true - Each stop (from Load) becomes a service with
id = Load.Idand coordinates.
Optional parameters like completion_time and configuration flags (e.g., routing.calc_points) can be added.
3. VRP Request
- A synchronous call is made to the
/vrpendpoint:POST /vrp?key=...
This is ideal for small problems (solvable within ~10 seconds). - For large problems, use
/vrp/optimize?key=...and poll the solutionvia /vrp/solution/{jobId}?key=....
4. Extract Initial Sequence
The response from GraphHopper provides a sequence of stops (by id).
- Extract routes[0].activities and reorder based on the
id(matching Load Ids). - Assign a Route Sequence to each Load.
5. Handle Business Rules
If any high-priority Loads exist, re-order them before finalizing the sequence.
6. Routing
The final sequence is sent to the /route endpoint to compute the closed-loop route (from depot → stops → depot):
- Points are structured as:
[depotLon, depotLat], [lon, lat], [depotLon, depotLat] - Call
/routewith the required vehicle profile and snap_preventions (e.g.,motorway,ferry,tunnel).
7. Write Back Results
- Trip:
Total_Distance__c(distance in kilometers)Estimated_Driving_Time__c(formatted time)
- Load:
- Update the
Route_Sequence__cfield according to the final order.
- Update the
8. Fallback
If the /route call fails or returns no paths, fallback to the VRP solution’s distance/time (solution.distance, solution.transport_time).
Field Mapping
| FTM Field | GraphHopper API Field | Purpose |
| Warehouse Coordinates | vehicle start/end | Used as depot coordinates |
| Load Coordinates | service coordinates | Used as stop coordinates |
| VRP Solution | routes[0].activities[].id | Order of loads/services |
| Route Distance | paths[0].distance | Total distance (meters) → km |
| Route Time | paths[0].time | Total travel time (ms) → formatted |
| Fallback VRP Solution | solution.distance | Distance (m) → km |
| Fallback VRP Solution | solution.transport_time | Time (s) → formatted |
Error Handling & Observability
- Log status codes and response bodies for non-200 responses.
- Add retry logic for rate-limited (429) or server errors (5xx).
- Optionally, create a Platform Event or custom Integration_Log__c for error tracking.
FAQs
- When should I use /vrp vs /vrp/optimize?
– Use /vrp for small, fast problems (< 10 stops).
– Use /vrp/optimize for large problems, then poll with/vrp/solution/{jobId}.
- Can I pass shipments instead of services?
Yes, if a stop has both pickup and delivery, use shipments to ensure proper sequencing (pickup before delivery). - How do I respect truck restrictions?
Use the small_truck or truck profile, or set up a custom profile if your plan supports it. - How do I track API credit usage?
Monitor theX-RateLimit-*headers in the response for credits/usage. You can log these per request. - Can I avoid specific roads (e.g., ferries, motorways)?
Yes, use thesnap_preventionsparameter to avoid certain road types.
Need Help?
For questions, changes, or to activate your GraphHopper integration, email [email protected]

